
If you are a recent graduate or a young worker from the province, looking for your first job or having been looking for work for a long time in the Manila metropolitan area, offers may exist, but these are usually contractual agreements. Some of you may be hesitant to take on these positions, while some have no option but to accept the job. This reality is reflected in many testimonies of YCW members in Valenzuela City.
YCW Philippines, together with other trade unions and organizations, is calling for an “ENDO” of the contractualization system in the Philippines. Contractualization is actually bad not just for workers but for all Filipinos. It may take a decade of struggle, but right now, we can already do something about it.
It is always important to know your rights as a worker. Being aware of these rights, we can better advocate for our well-being and demand decent salary and just work in our workplaces together with other workers.
What is contractualization in the Philippines?
It is an employment practice that consists in hiring workers on fixed-term contracts, usually short-term, that end before six months have elapsed, hence the term “endo” or end of contract. Companies want to circumvent a provision of the Labor Code which states that employees who have worked in a company for six months must be regularized.
Contractualization has long been a subject of concern and advocacy for the YCW. It is linked to the IYCW international campaign on precarious work. For the YCW, contractualization violates workers’ rights to organize and collectively bargain for higher wages, social security and health benefits, better terms of employment, and safe working conditions. It exposes workers to unfair labor practices and violations of their rights.
The reality of contract workers in Valenzuela City
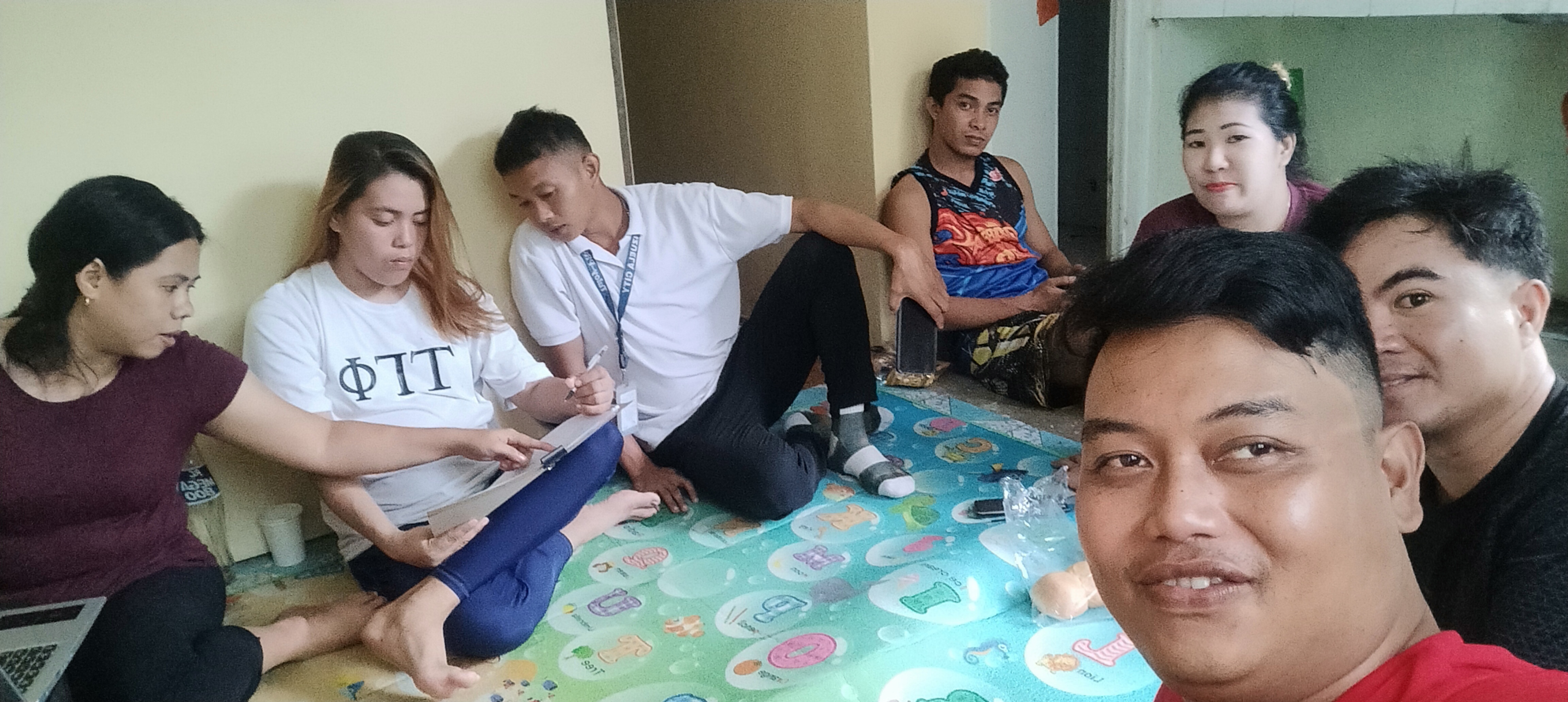

During his field mission in August 2023, IYCW-ASPAC coordinator Rony Robiansyah noted some challenging realities facing young workers who are working in the Valenzuela factories.
Competition for jobs is fierce. Two years after being hit by the Covid-19 pandemic, the large number of new graduates entering the workforce and the lack of job opportunities add to the already existing tough competition between workers to find work. This situation is an opportunity for multinational companies to recruit workers on short-term contracts.
Young workers are usually employed for a short period, and the employer-employee relationship is distant. Workers have no direct contact with employers as they work through recruitment agencies. Contract workers often perform manual work, and companies do not pay attention to worker safety. When work accidents occur, workers do not receive fair compensation from their employers.
Some key points of concern for contract workers in Valenzuela City include: long working hours (10-12 hours); low income compared to basic daily expenses (food, transport, rent, etc.); unpaid overtime; inability of contract workers to participate in and join a trade union; outsourcing of company activities via manpower agencies; some companies do not pay social security benefits, health insurance and housing allowances; no work-no pay, even on special holidays; expensive and high-standard requirements to apply for a job.
Breaking the taboo of contractualization
Some groups or individuals claim that contractualization is actually good for the workers and for the Philippines. In their view, contractualization enables employers to increase their profits and expand their businesses, which in turn leads to the hiring of more contract workers and contributes to the country’s economic growth. Otherwise, if the government abolishes contractualization, they believe that many companies will shut down. Shutting down means that the profits of the employer will plummet, many workers will be laid off, and the Philippine economy will collapse. But this argument is a capitalistic perspective and only serves the interests of the companies.
In fact, allowing employers to further exploit workers through contractualization and cheap labor practices affects productivity and reduces workers’ purchasing power. As a result, the society’s development cycle is hampered. If more workers become poorer, the country becomes poorer too. The gap between rich and poor only widens. What's more, contractualization weakens solidarity between workers, and hence collective action.
Educating, organizing, mobilizing and building a network of workers

YCW Philippines regularly holds training discussions on workers’ fundamental rights. During the visit of the IYCW-ASPAC coordinator, the activity was attended by representatives of YCW-Philippines National Secretariat, as well as invited contract workers and YCW members from Valenzuela City. It was also attended by the network organization Women WISE, an organization working with women workers fighting for employment, empowerment and emancipation.
These training sessions cover a range of topics relating to labor rights, the right to employment, and the steps to be taken if workers’ rights are violated. Significantly, YCW Philippines and Women Wise have agreed to continue working together in Valenzuela City to organize, raise awareness and support young workers, women workers, and workers in general.












 English
English  Español
Español  Français
Français